The Rose Window, also alternatively called a wheel window, refers to a circular window with mullions and traceries generally radiating from the center, and filled with stained glass. The name comes from the likeness of the window with its decorative elements to the rose and its petals. It originated around the 10th century during the Romanesque period, from the Roman oculus, Italy.

The Pantheon Oculus, Rome, Italy
As time progressed, the idea of the circular window portraying a thematic idea or motif came about and became an identifying marker for Gothic architecture, mainly churches. The key examples of rose windows in the early periods are the west Rose of the Cathedral of Mantes,France(1200) andthe west rose of Notre Dame, France(1220) .These examples all had the rose underneath a circle arch. It was also common to place the rose under a pointed arch as in the Cathedral of Reims, France (1230).
According to Britannica, In the 12th century, rose windows were used mainly at the west end of the nave and the end of the transepts. The nave was the central and principal part of a Christian church, extending from the entrance (the narthex) to the transepts (transverse aisle crossing the nave in front of the sanctuary in a cruciform church) or, in the absence of transepts, to the chancel (area around the altar). The introduction of developed bar tracery in the 13th century gave a compelling impetus to rose window design.
Tracery refers to the bars or ribs used decoratively in windows or other openings. This was developed in Europe during the Gothic period For rose windows the tracery consisted of a series of radiating forms, each of which was tipped by a pointed arch at the outside of the circle. The bars between these forms were joined at the centre by a pierced circle of stone, and the forms themselves frequently were treated like little traceried windows with subsidiary, subdividing bars, arches and foiled circles.
In Trinidad there are various examples of this architectural feature across time periods such as the Cathedral Church of Holy Trinity built between 1816 and 1823 which possesses a Rose Window in its western gable.


Photograph of the stained glass rose window located in the western gable of the Holy Trinity Cathedral
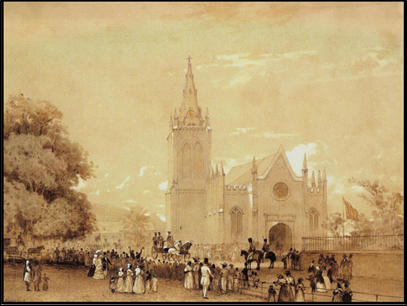
Depiction of the wedding of Lord Harris to Sarrah Cummins, with another view of the rose window on the western gable of the Holy Trinity Cathedral.
The St. Francis of Assisi RC Church, built in 1902 and located in Belmont, has a lovely rose window located in its eastern gable with marvellous tracery patterns indicative of the Romanesque architectural style.

Photograph of rose window with tracery located in the eastern gable of the St. Francis of Assisi RC Church
The All Saint’s Anglican Church built in 1846 in the Neo-Gothic Revival architectural style possesses five rose windows one on each façade of the building with two rose windows for its two eastern facades depicted below.
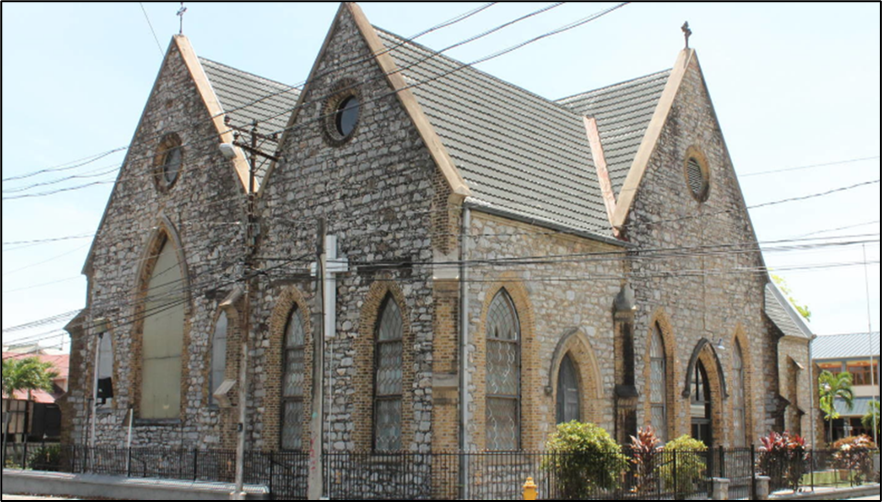

Photograph depciting the All Saint’s Anglican Church showing three rose windows, two of which are in the church’s two eastern facades.
Our final mention, is the breathtaking, Our Lady of Montserrat RC Church. Located in Tortuga and built in 1878, is a wooden church designed in the Neo-Romanesque style, and possesses a stained glass rose window in its northern facing gable.
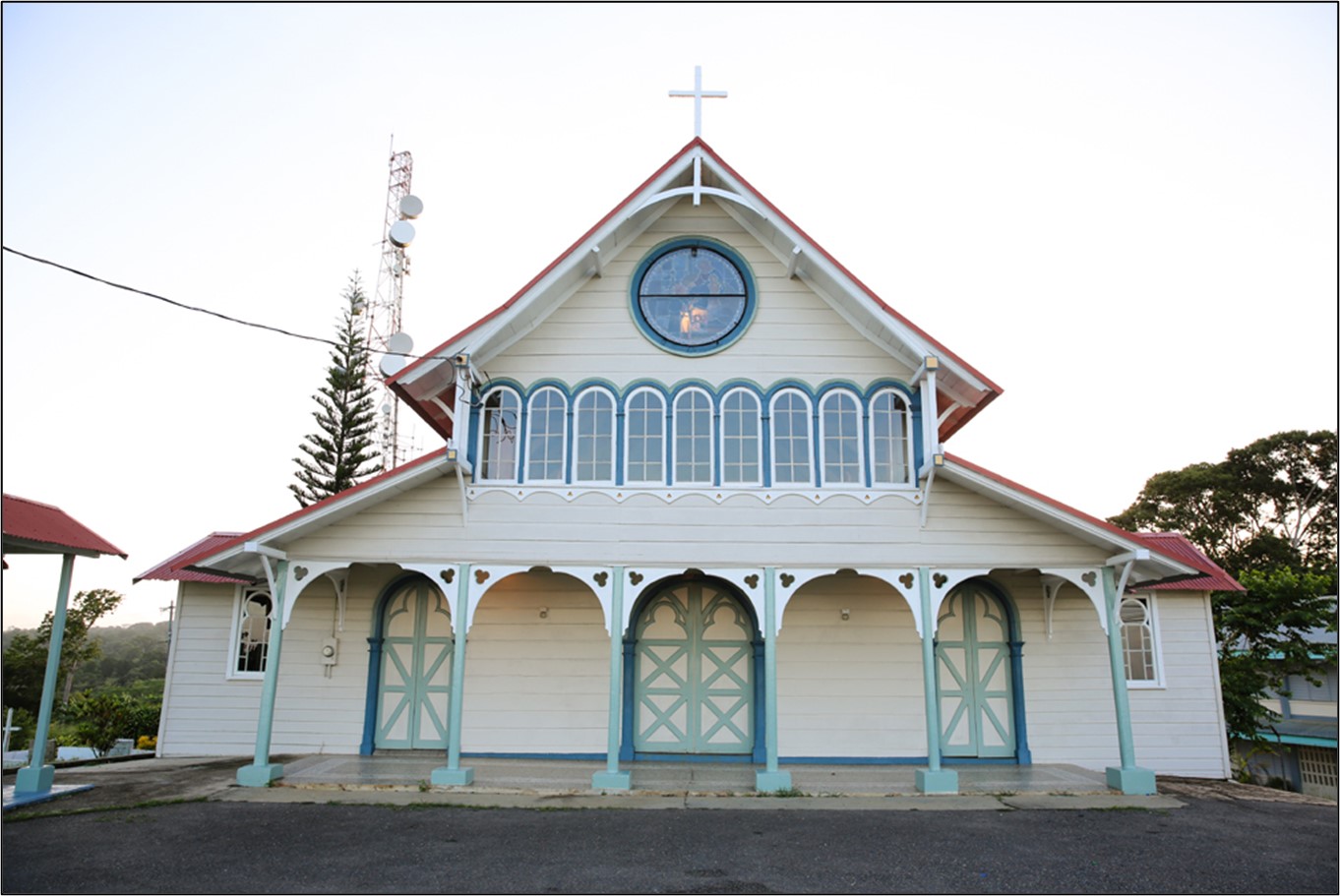

Photograph of the Stained glass rose window located in the northern gable of the Our Lady of Montserrat RC Church.
Sources
https://www.friendsofnotredamedeparis.org/cathedral/artifacts/rose-windows/
Brittanica.com/technology/rosewindows
Britannica.com/architecture/nave
Rose Windows and other Follies: Alternative Architecture in the Seventeenth-Century Pennines, Cambridge Press University, April 2016. Cambridge
Image Sources
GJCL Classical Art History: The Roman Masterpiece to All Gods (gjclarthistory.blogspot.com)
M.J. Cazabon
National Trust of Trinidad and Tobago

